Spatial data and the tidyverse
🌐
new tools for geocomputation with R
Robin Lovelace and Jakub Nowosad
2017-09-05
This mini-workshop will introduce you to recent developments that enable work with spatial data 'in the tidyverse'. By this we mean handling spatial datasets using functions (such as %>% and filter()) and concepts (such as type stability) from R packages that are part of the metapackage tidyverse, which can now be installed from CRAN with the following command:
install.packages("tidyverse")This functionality is possible thanks to sf, a recent package (first release in 2016) that implements the open standard data model simple features. Get sf with:
install.packages("sf")The workshop will briefly introduce both packages (which should be installed on your computer before attending) before demonstrating how they can work in harmony using a dataset from the spData package, which can be installed with:
install.packages("spData")The workshop is based on our work on the forthcoming book Geocomputation with R - please take a look at the book and its source code prior to the workshop here: github.com/Robinlovelace/geocompr.
Context
- Software for 'data science' is evolving
- In R, packages ggplot2 and dplyr have become immensely popular and now they are a part of the tidyverse
- These packages use the 'tidy data' principles for consistency and speed of processing (from
vignette("tidy-data")):
- Each variable forms a column.
- Each observation forms a row.
- Each type of observational unit forms a table
- Historically spatial R packages have not been compatible with the tidyverse
Enter sf
- sf is a recently developed package for spatial (vector) data
- Combines the functionality of three previous packages: sp, rgeos and rgdal
- Has many advantages, including:
- Faster data I/O
- More geometry types supported
- Compatibility with the tidyverse
That's the topic of this workshop
Geocomputation with R
- A book we are working on for CRC Press (to be published in 2018)
- Chapters 3
and 4of this book form the basis of the worked examples presented here
Prerequisites
- Install the required packages. You need a recent version of the GDAL, GEOS, Proj.4, and UDUNITS libraries installed for this to work on Mac and Linux. More information on that at https://github.com/r-spatial/sf#installling.
devtools::install_github("robinlovelace/geocompr")- Load the ones we need:
library(spData)library(dplyr)library(sf)- Check it's all working, e.g. with this command:
world %>% plot()Reading and writing spatial data
library(sf)library(spData)vector_filepath = system.file("shapes/world.gpkg", package = "spData")vector_filepath## [1] "/home/robin/R/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu-library/3.4/spData/shapes/world.gpkg"world = st_read(vector_filepath)## Reading layer `wrld.gpkg' from data source `/home/robin/R/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu-library/3.4/spData/shapes/world.gpkg' using driver `GPKG'## Simple feature collection with 177 features and 10 fields## geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON## dimension: XY## bbox: xmin: -180 ymin: -90 xmax: 180 ymax: 83.64513## epsg (SRID): 4326## proj4string: +proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defsCounterpart to st_read() is the st_write function, e.g. st_write(world, 'data/new_world.gpkg'). A full list of supported formats could be found using sf::st_drivers().
Structure of the sf objects
world## Simple feature collection with 177 features and 10 fields## geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON## dimension: XY## bbox: xmin: -180 ymin: -90 xmax: 180 ymax: 83.64513## epsg (SRID): 4326## proj4string: +proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs## First 3 features:## iso_a2 name_long continent region_un subregion type## 1 AF Afghanistan Asia Asia Southern Asia Sovereign country## 2 AO Angola Africa Africa Middle Africa Sovereign country## 3 AL Albania Europe Europe Southern Europe Sovereign country## area_km2 pop lifeExp gdpPercap geom## 1 652270.1 31627506 60.37446 1844.022 MULTIPOLYGON (((61.21081709...## 2 1245463.7 24227524 52.26688 6955.960 MULTIPOLYGON (((16.32652835...## 3 29694.8 2893654 77.83046 10698.525 MULTIPOLYGON (((20.59024743...class(world)## [1] "sf" "data.frame"Structure of the sf objects
world$name_long## [1] Afghanistan Angola Albania ## 177 Levels: Afghanistan Albania Algeria Angola Antarctica ... Zimbabweworld$geom## Geometry set for 177 features ## geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON## dimension: XY## bbox: xmin: -180 ymin: -90 xmax: 180 ymax: 83.64513## epsg (SRID): 4326## proj4string: +proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs## First 3 geometries:## MULTIPOLYGON (((61.2108170917257 35.65007233330...## MULTIPOLYGON (((16.326528354567 -5.877470391466...## MULTIPOLYGON (((20.5902474301049 41.85540416113...sf vs sp
- The sp package is a predecessor of the sf package
- Together with the rgdal and rgeos package, it creates a powerful tool to works with spatial data
- Many spatial R packages still depends on the sp package, therefore it is important to know how to convert sp to and from sf objects
library(sp)world_sp = as(world, "Spatial")world_sf = st_as_sf(world_sp)The structures in the sp packages are more complicated -
str(world_sf)vsstr(world_sp)Moreover, many of the sp functions are not "pipeable" (it's hard to combine them with the tidyverse)
world_sp %>% filter(name_long == "England")Error in UseMethod("filter_") :
no applicable method for 'filter_' applied to an object of class "c('SpatialPolygonsDataFrame', 'SpatialPolygons', 'Spatial')"
Non-spatial operations on the sf objects
world %>% left_join(worldbank_df, by = "iso_a2") %>% select(name_long, pop, pop_growth, area_km2) %>% arrange(area_km2) %>% mutate(pop_density = pop/area_km2) %>% rename(population = pop)## Simple feature collection with 177 features and 5 fields## geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON## dimension: XY## bbox: xmin: -180 ymin: -90 xmax: 180 ymax: 83.64513## epsg (SRID): 4326## proj4string: +proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs## First 20 features:## name_long population pop_growth area_km2## 1 Luxembourg 556319 2.35697870 2416.870## 2 Northern Cyprus NA 2.36947994 3786.365## 3 Palestine 4294682 2.95799495 5037.104## 4 Cyprus 1153658 1.04614274 6207.006## 5 Vanuatu 258883 2.23347721 7490.040## 6 Trinidad and Tobago 1354483 0.46197935 7737.810## 7 Puerto Rico 3534888 -1.63278794 9224.663## 8 Lebanon 5612096 5.96751825 10099.003## 9 Brunei Darussalam 417394 1.42240299 10700.334## 10 Kosovo NA 2.36947994 11230.333## 11 Qatar 2172065 3.31278379 11327.855## 12 French Southern and Antarctic Lands NA NA 11602.572## 13 Jamaica 2720554 0.36303364 12460.587## 14 Montenegro 621810 0.09702201 13443.720## 15 The Gambia 1928201 3.23199269 14031.284## 16 Timor-Leste 1212107 2.45302951 14714.931## 17 Bahamas 383054 1.37024992 15584.791## 18 Falkland Islands NA NA 16363.799## 19 Kuwait 3753121 4.34085090 16652.120## 20 Swaziland 1269112 1.46612234 18118.634## pop_density geom## 1 230.18155 MULTIPOLYGON (((6.043073357...## 2 NA MULTIPOLYGON (((32.73178022...## 3 852.60939 MULTIPOLYGON (((35.54566531...## 4 185.86384 MULTIPOLYGON (((33.97361657...## 5 34.56363 MULTIPOLYGON (((167.8448767...## 6 175.04734 MULTIPOLYGON (((-61.68 10.7...## 7 383.19968 MULTIPOLYGON (((-66.2824344...## 8 555.70792 MULTIPOLYGON (((35.82110070...## 9 39.00757 MULTIPOLYGON (((114.2040165...## 10 NA MULTIPOLYGON (((20.76216 42...## 11 191.74549 MULTIPOLYGON (((50.81010827...## 12 NA MULTIPOLYGON (((68.935 -48....## 13 218.33273 MULTIPOLYGON (((-77.5696007...## 14 46.25282 MULTIPOLYGON (((19.80161339...## 15 137.42156 MULTIPOLYGON (((-16.8415246...## 16 82.37259 MULTIPOLYGON (((124.9686824...## 17 24.57871 MULTIPOLYGON (((-77.53466 2...## 18 NA MULTIPOLYGON (((-61.2 -51.8...## 19 225.38398 MULTIPOLYGON (((47.97451907...## 20 70.04457 MULTIPOLYGON (((32.07166548...Non-spatial operations
world_cont = world %>% group_by(continent) %>% summarize(pop_sum = sum(pop, na.rm = TRUE))## Simple feature collection with 8 features and 2 fields## geometry type: GEOMETRY## dimension: XY## bbox: xmin: -180 ymin: -90 xmax: 180 ymax: 83.64513## epsg (SRID): 4326## proj4string: +proj=longlat +datum=WGS84 +no_defs## # A tibble: 8 x 3## continent pop_sum geom## <fctr> <dbl> <simple_feature>## 1 Africa 1147005839 <MULTIPOLYGON...>## # ... with 7 more rows- The
st_set_geometryfunction can be used to remove the geometry column:
world_df =st_set_geometry(world_cont, NULL)class(world_df)## [1] "tbl_df" "tbl" "data.frame"Spatial operations
It's a big topic which includes:
- Spatial subsetting
- Spatial joining/aggregation
- Topological relations
- Distances
- Spatial geometry modification
- Raster operations (map algebra)
See Chapter 4 of Geocomputation with R
Spatial subsetting
lnd_buff = lnd[1, ] %>% st_transform(crs = 27700) %>% # uk CRS st_buffer(500000) %>% st_transform(crs = 4326)near_lnd = world[lnd_buff, ]plot(near_lnd$geom)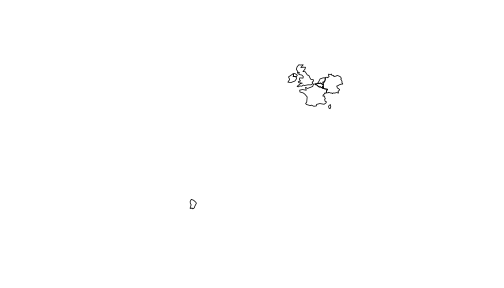
- What is going with the country miles away?
Multi-objects
Some objects have multiple geometries:
st_geometry_type(near_lnd)## [1] MULTIPOLYGON MULTIPOLYGON MULTIPOLYGON MULTIPOLYGON MULTIPOLYGON## [6] MULTIPOLYGON MULTIPOLYGON## 18 Levels: GEOMETRY POINT LINESTRING POLYGON ... TRIANGLEWhich have more than 1?
data.frame(near_lnd$name_long, sapply(near_lnd$geom, length))## near_lnd.name_long sapply.near_lnd.geom..length.## 1 Belgium 1## 2 Germany 1## 3 France 3## 4 United Kingdom 2## 5 Ireland 1## 6 Luxembourg 1## 7 Netherlands 1Subsetting contiguous polygons
near_lnd_new = world %>% st_cast(to = "POLYGON") %>% filter(st_intersects(., lnd_buff, sparse = FALSE))plot(near_lnd_new$geometry)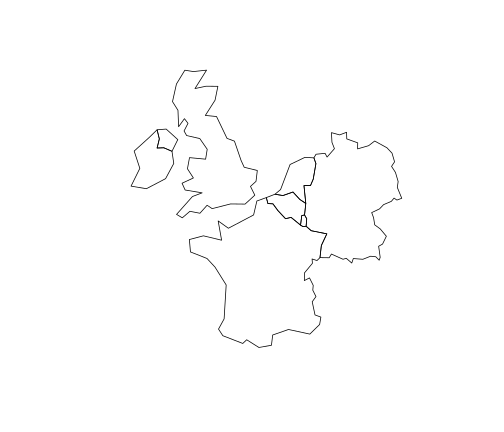
CRS
na_2163 = world %>% filter(continent == "North America") %>% st_transform(2163) #US National Atlas Equal Areast_crs(na_2163)## $epsg## [1] 2163## ## $proj4string## [1] "+proj=laea +lat_0=45 +lon_0=-100 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +a=6370997 +b=6370997 +units=m +no_defs"## ## attr(,"class")## [1] "crs"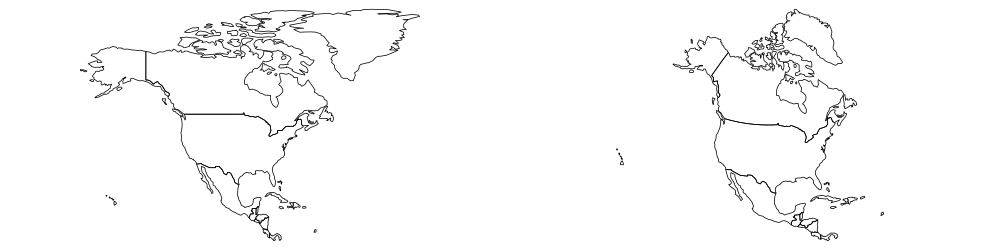
Basic maps
- Basic maps of
sfobjects can be quickly created using theplot()function:
plot(wrld[0])plot(wrld["pop"])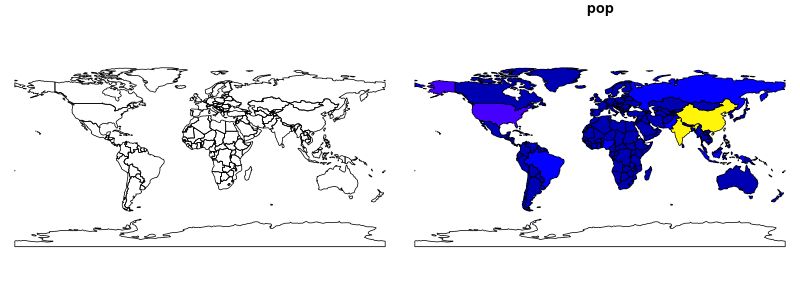
tmap
https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/tmap/vignettes/tmap-nutshell.html
library(tmap)tmap_mode("plot") #check the "view"tm_shape(world, projection="wintri") + tm_polygons("lifeExp", title=c("Life expactancy"), style="pretty", palette="RdYlGn", auto.palette.mapping=FALSE) + tm_style_grey()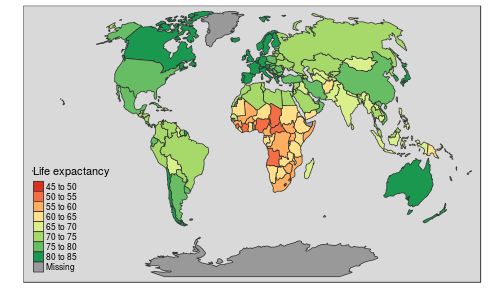
leaflet
library(leaflet)leaflet(world) %>% addTiles() %>% addPolygons(color = "#444444", weight = 1, fillOpacity = 0.5, fillColor = ~colorQuantile("YlOrRd", lifeExp)(lifeExp), popup = paste(round(world$lifeExp, 2)))Raster data in the tidyverse
Raster data is not yet closely connected to the tidyverse, however:
- Some functions from the raster package works well in
pipes - You can convert vector data to the
Spatial*form usingas(my_vector, "Spatial")before working on raster-vector interactions - There are some initial efforts to bring raster data closer to the tidyverse, such as tabularaster, sfraster, or fasterize
- The development of the stars, package focused on multidimensional, large datasets should start soon. It will allow pipe-based workflows
Geocomputation with R
The online version of the book is at http://robinlovelace.net/geocompr/ and its source code at https://github.com/robinlovelace/geocompr.
We encourage contributions on any part of the book, including:
- Improvements to the text, e.g. clarifying unclear sentences, fixing typos (see guidance from Yihui Xie)
- Changes to the code, e.g. to do things in a more efficient way
- Suggestions on content (see the project's issue tracker and the work-in-progress folder for chapters in the pipeline)
Please see our_style.md for the book's style.